| Index | wersja polska
|
UPDATE: The information shown here was initially obtained through reverse engineering and therefore may differ from the contents of the original datasheet published on 2011/12/22.
The cartridge is designed as removable storage medium for the Elektronika MK-90 pocket computer. The RAM inside the cartridge is accessed by the computer through a serial interface with a transfer rate of ca. 100kbits/s. Although there's only 10kB RAM on-board, the built-in controller chip is capable of addressing up to 64kB of RAM.
The cartridge consists of 5 static RAM chips KA537RU10 with battery backup and a KA1835VG2 controller.

| Pin | Symbol | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BATT. | plus pole of an internal 3V lithium battery |
| 2 | VCC | positive supply voltage +5V |
| 3 | CLOCK | serial clock input |
| 4 | DATA | serial data input/output |
| 5 | SELECT | chip select input |
| 6 | GND | ground |
Data written to the cartridge change at rising edges of the CLOCK pulses, and are shifted-in on falling edges of the CLOCK pulses beginning with the most significant bit.
The first transmitted byte after the SELECT high to low transition is the command op-code.
Following the op-code, any addresses and data are then transferred.
The waveform below shows an example of Write Address command (signals SELECT, CLOCK, DATA).
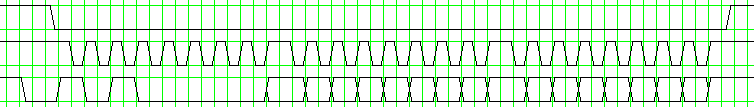
Data read from the cartridge change at falling edges of the CLOCK pulses, and are sampled at rising edges of the CLOCK pulses.
The waveform below shows an example of Read Data command.
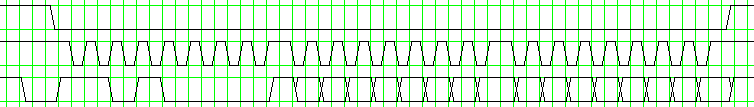
| Op-code | Command name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | Read Status | |
| 0x10 | Read Postdecrement | Read any amount of data bytes from the cartridge starting from the location pointed to by the address register. The address register is decremented after each received byte. This command is not used by the MK-90. |
| 0x20 | Erase Postdecrement | Write any amount of data bytes to the cartridge starting from the location pointed to by the address register. The address register has to be initialised to 0xFFFF (otherwise the command is ignored) and is decremented after each transmitted byte. This command is used by the MK-90 to clear the cartridge RAM with spaces when formatting with INIT. |
| 0x80 | Lock | |
| 0x90 | Unlock | |
| 0xA0 | Write Address | Write the 16-bit address register, the most significant byte first. |
| 0xB0 | Read Address | Read the 16-bit address register, the most significant byte first. This command is not used by the MK-90. |
| 0xC0 | Write Postincrement | Write any amount of data bytes to the cartridge starting from the location pointed to by the address register. The address register is incremented after each transmitted byte. |
| 0xD0 | Read Postincrement | Read any amount of data bytes from the cartridge starting from the location pointed to by the address register. The address register is incremented after each received byte. |
| 0xE0 | Write Postdecrement | Write any amount of data bytes to the cartridge starting from the location pointed to by the address register. The address register is decremented after each transmitted byte. Not used by the MK-90. |
The lower four bits of the command op-code are "don't care" values. All other op-codes not listed in the above table are ignored along with any following data.